126. 单词接龙 II(Hard)
题目描述
给定两个单词(beginWord 和 endWord)和一个字典 wordList,找出所有从 beginWord 到 endWord 的最短转换序列。转换需遵循如下规则:
- 每次转换只能改变一个字母。
- 转换后得到的单词必须是字典中的单词。
说明:
- 如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回一个空列表。
- 所有单词具有相同的长度。
- 所有单词只由小写字母组成。
- 字典中不存在重复的单词。
- 你可以假设 beginWord 和 endWord 是非空的,且二者不相同。
样例
Input:
beginWord = "hit",
endWord = "cog",
wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"]
Ouptut:
[
["hit","hot","dot","dog","cog"],
["hit","hot","lot","log","cog"]
]
题解
单层 BFS
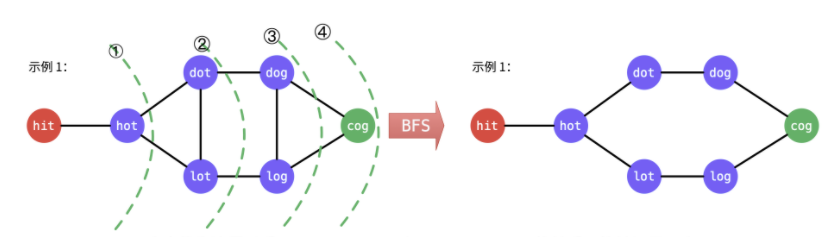
单层无优化 BFS 代码
这里的图的建立是通过 层次遍历法 建立的关系。
# 超时 20/39
from collections import deque
def diffOneletter(word1, word2):
c = 0
for i in range(len(word1)):
if word1[i] != word2[i]:
c += 1
return c == 1
class Solution:
def findLadders(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> List[List[str]]:
queue = deque()
queue.append([beginWord, [beginWord]])
ans = []
find = False
while queue:
for _ in range(len(queue)):
word, path = queue.popleft()
if word == endWord:
ans.append(path[:])
find = True
for i in range(len(wordList)): # 通过不停的试建立了 字与字的关系
if wordList[i] not in path and diffOneletter(word, wordList[i]):
queue.append([wordList[i], path + [wordList[i]]])
if find:
break
return ans
代码实现了基本的BFS思想,但是存在很多优化的点:
diffOneletter存在大量重复计算- 由于是要求出所有最短路径集合,而不是最短步数,如果不加剪枝策略的话,一定会超时。
单层BFS优化①
参考:LeetCode 官方题解的思路
这里的优化体现在,首先根据 wordList 字典来 建立一张图,使用邻接矩阵实现。
edges = defaultdict(set)
for word1 in wordList:
for word2 in wordList:
if diffOneletter(word1, word2):
edges[word1].add(word2)
edges[word2].add(word1)
# 超时 32/39
from collections import deque, defaultdict
def diffOneletter(word1, word2):
c = 0
for i in range(len(word1)):
if word1[i] != word2[i]:
c += 1
return c == 1
class Solution:
def findLadders(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> List[List[str]]:
# 当 endWord 不存在的时候,就返回空数组
if endWord not in wordList:
return []
# 创建邻接矩阵
if beginWord not in wordList:
wordList.append(beginWord)
edges = defaultdict(list)
for i in range(len(wordList)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(wordList)):
if diffOneletter(wordList[i], wordList[j]):
edges[wordList[i]].append(wordList[j])
edges[wordList[j]].append(wordList[i])
queue = deque()
queue.append([beginWord])
visited = set()
visited.add(beginWord)
ans = []
find = False
while queue:
subvisited = set() # 集合记录下一层的节点,可以做到去重
for _ in range(len(queue)):
path = queue.popleft()
cur_word = path[-1]
if cur_word == endWord:
ans.append(path[:]) # 这里使用 path 每次直接保存了路径,但是很多解法认为这样做法会极大消耗空间,所以一般是通过 BFS 建立词与词的关系图,然后再使用 DFS 寻找最优路径。
find = True
for word in edges[cur_word]:
if word not in visited and :
queue.append(path + [word])
subvisited.add(word)
for word in subvisited: # 同一层遍历结束后,再加入
visited.add(word)
if find:
break
return ans
这样优化的 Python 代码无法AC,但是等价的 Java 是可以的,不过也是属于极限状态。
为了继续优化,我们参考 详细通俗的思路分析,多解法 记录每一个节点的层信息,当 abc 出现第二次的时候,由于曾经访问过,就不应该继续搜索了。

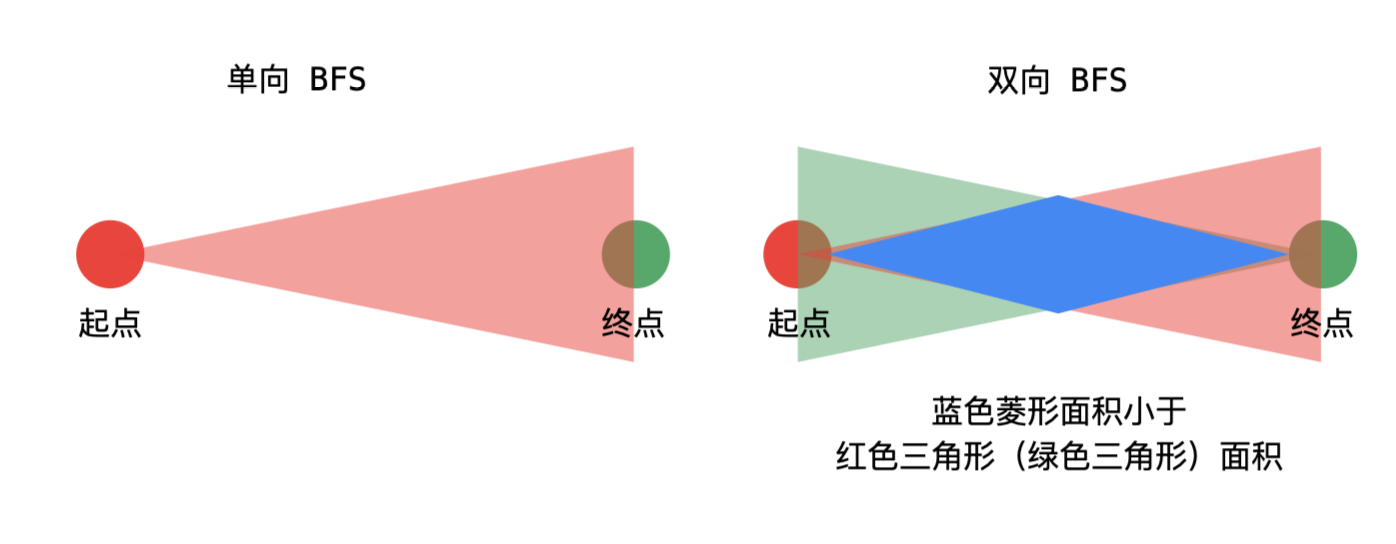
双向广搜
def backtracking(src, dst, successors, path, ans):
if src == dst:
ans.append(path[:])
return
for cur in successors[src]:
path.append(cur)
backtracking(cur, dst, successors, path, ans)
path.pop()
class Solution:
def findLadders(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> List[List[str]]:
if endWord not in wordList: # 如果endWord不存在的话,一定是出不来答案
return []
q1, q2 = {beginWord}, {endWord} # 这里注意不能使用 list 会超时的,必须使用 set 哈希表
notVisitedWords = set(wordList) # 记录了所有没有访问过的单词
if beginWord in notVisitedWords: # beginWord 不一定会在 wordList 中
notVisitedWords.remove(beginWord)
notVisitedWords.remove(endWord)
successors = defaultdict(set) # bfs 用来记录字典的图关系
reverse = False
found = False
while q1: # 先使用 q1
visitedWords = set()
for curWord in q1:
for j in range(len(curWord)):
ch = curWord[j]
for k in range(26):
nextList = list(curWord)
nextList[j] = chr(ord('a') + k)
nextWord = ''.join(nextList)
if nextWord in q2: # 如果在q2中出现过,证明已经找到了
found = True
if not reverse:
successors[curWord].add(nextWord)
else:
successors[nextWord].add(curWord)
if nextWord in notVisitedWords: # 如果nextWord是合法的
if not reverse:
successors[curWord].add(nextWord)
else:
successors[nextWord].add(curWord)
visitedWords.add(nextWord) # 记录访问过的单词
if found: # 剪枝
break
for word in visitedWords: # 将所有访问过的节点从未访问过的节点中去除
if word in notVisitedWords:
notVisitedWords.remove(word)
if len(visitedWords) <= len(q2): # 根据节点的大小调整搜索的方向
q1 = visitedWords # 记录从左搜索
else:
reverse = not reverse # 翻转,换个方向搜索
q1 = q2
q2 = visitedWords
ans = []
if found: # 使用 dfs 搜索出最优路径
path = [beginWord]
backtracking(beginWord, endWord, successors, path, ans)
return ans